What is a Domain Name: A Step-by-Step Guide
Introduction
Here you go explanation of “what is a domain name: a step-by-step guide” In the vast landscape of the internet, there exists a fundamental concept that serves as the backbone of every website and online presence – the domain. From personal blogs to multinational corporations, understanding what a domain is and how it functions is essential for anyone navigating the digital realm. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of domains, exploring their definition, purpose, components, registration process, and much more, step by step.
Defining a Domain
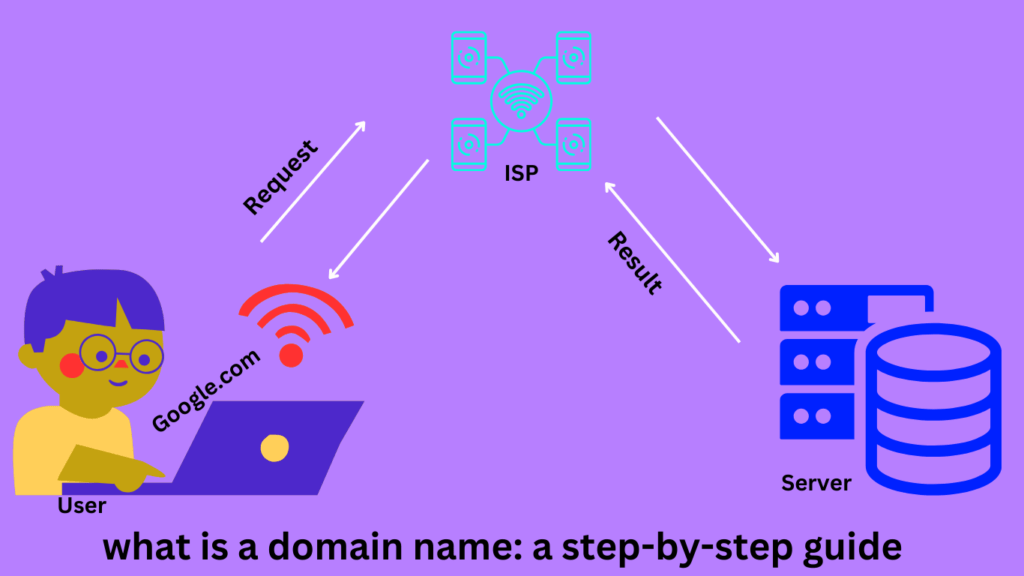
At its core, a domain is a human-readable address that represents a unique location on the internet. It serves as the gateway for users to access websites, sending requests to specific servers and retrieving the desired content. Think of it as the digital equivalent of a physical address, guiding visitors to the online destination they seek.
Components of a Domain
Domains consist of two main components: the domain name and the domain extension. The domain name is the customizable part of the address, typically representing the brand, organization, or content of the website. For example, in the domain “example.com,” “example” is the domain name. The domain extension, also known as a top-level domain (TLD), follows the domain name and indicates the type or purpose of the website, such as “.com,” “.org,” or “.net.”
Understanding Domain Name System (DNS)
Behind the scenes, the Domain Name System (DNS) plays a crucial role in translating human-readable domain names into machine-readable IP addresses. When a user enters a domain name into their web browser, the DNS servers resolve that name to the corresponding IP address of the web server hosting the website. This process enables seamless communication across the internet, allowing users to access websites using familiar domain names.
Registering a Domain
To acquire a domain for your website, you must register it through a domain registrar – a company authorized to manage domain registrations. The registration process involves selecting an available domain name, choosing a suitable domain extension, providing contact information, and completing the payment for registration fees. Once registered, you gain exclusive rights to use that domain for a specified period, typically renewable on an annual basis.
Popular Domain Register site
godady.com
namecheap.com
Domain Availability and Selection
Selecting the right domain name is crucial for establishing your online identity and attracting visitors to your website. However, finding an available domain name can be challenging, especially considering the millions of domains already registered. It’s essential to brainstorm creative, memorable names relevant to your brand or content while checking for availability using domain registrar websites or specialized tools.
Domain Privacy and WHOIS Protection
When registering a domain, you’ll be required to provide contact information that becomes publicly accessible through the WHOIS database. This includes your name, address, phone number, and email address. However, for privacy and security reasons, many registrars offer WHOIS privacy protection services, masking your personal information and replacing it with their own. Consider opting for this service to safeguard your privacy and prevent spam or unwanted solicitations.
Managing DNS Settings (what is a domain name: a step-by-step guide)
After registering a domain, you’ll need to configure its DNS settings to point to the appropriate web servers hosting your website. This involves setting up DNS records, such as A records for linking the domain to an IP address, MX records for email services, and CNAME records for aliasing one domain to another. DNS management tools provided by your domain registrar or web hosting provider simplify this process, allowing you to customize settings according to your requirements.
Renewing and Transferring Domains
Domain registrations are typically valid for one year, after which they must be renewed to maintain ownership and continuity of service. Most registrars offer auto-renewal options to prevent accidental expiration of domains. Additionally, if you wish to transfer your domain to another registrar or a different owner, you can initiate the transfer process by unlocking the domain and obtaining an authorization code, adhering to specific transfer guidelines outlined by ICANN, the governing body of domain registrations.
Domain Branding and Strategy
Your domain plays a significant role in shaping your online branding and marketing strategy. It’s essential to choose a domain name that reflects your brand identity, resonates with your target audience, and is easy to remember and spell. Consider factors such as keyword relevance, domain length, and brand consistency when crafting your domain strategy. Furthermore, securing multiple domain variations and relevant extensions can protect your brand and expand your online presence.
Legal Considerations and Trademarks
Conclusion :
In the digital landscape, domains serve as the gateway to the online world, providing unique addresses for websites to be accessed and discovered. Understanding the intricacies of domains – from their components and registration process to management and branding strategies – is essential for establishing a strong online presence. By following this step-by-step guide, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge and tools needed to navigate the domain ecosystem effectively and make informed decisions that propel your online endeavors forward.

Example domain of "What is a Domain Name:"
Table of Contents

Simple Resume Template Free Download
Why a Simple Resume Template Is Your Ticket to Success presently “Simple Resume Template Free Download” in the highly competitive

What is a Domain Name: A Step-by-Step Guide
What is a Domain Name: A Step-by-Step Guide Introduction Here you go explanation of “what is a domain name: a